A bill of lading is a legal document used in shipping. It acts like a receipt for the goods being shipped, a contract between the sender and the carrier, and also a document of title that proves who owns the goods. It is usually issued by the carrier (the shipping company) to the person or company sending the goods.
A bill of lading contains important information like:
- Name and address of the sender (shipper)
- Name and address of the receiver (consignee)
- Description of the goods (what’s inside the shipment)
- Quantity and weight of the goods
- Type of packaging (boxes, pallets, etc.)
- Name of the vessel or transport method
- Place of origin and destination
- Date of shipment
- Special instructions, if any
In this blog, Alliance Shipping will cover everything you need to know about a bill of lading. What it is, its importance, the types, and more!
What is a Bill of Lading
A bill of lading (often just called BOL or B/L) is a key document in shipping that helps move goods from one place to another. There are two parties agreeing to the terms in this document, i.e, shipper and consignee (customer).
The shipper is the person or company sending the goods. They are responsible for packing, labeling, and preparing the goods for transport. In most cases, the carrier (often working on behalf of the shipper) is the one who issues the bill of lading. It is issued once the carrier receives the goods and confirms their condition and quantity.
The consignee is the person or company receiving the goods, usually the buyer or end customer. When the shipment reaches its destination, the consignee uses the bill of lading to claim ownership and take delivery of the goods.
Types of B/L Document
There are three types of bill of lading, explained below:
1. Straight Bill of Lading
A straight bill of lading is made to a specific consignee and can’t be transferred to anyone else. The goods must be delivered only to the named person or company. This type of BOL is used when the buyer has already paid or when there’s no need for the goods to change hands, like in the case of returns or gifts. Since the ownership can’t be passed to another party during transit, it is considered a secure shipping method.
2. Order Bill of Lading
Another type is the order bill of lading, which allows ownership of the goods to be transferred while the shipment is still in transit. This makes it useful in international trade, especially when the goods might be sold again before they arrive. It’s also common in deals involving letters of credit, where the buyer and payment terms are still being finalized.
3. Bearer Bill of Lading
Lastly, a bearer bill of lading is the most flexible of all. It doesn’t name any consignee and instead allows whoever holds the original document to claim the goods. This type is rarely used because it carries a higher risk. For example, if the document is lost or stolen, whoever has it can collect the shipment. It’s only used in special situations and needs strict handling to avoid fraud or misuse.
Purpose & Importance of B/L Document
The bill of lading serves three main purposes.
- Proof of receipt: It confirms that the carrier has received the goods from the shipper in a specific condition and quantity.
- Agreement of shipping terms: It outlines the agreed-upon terms and conditions for the transportation of goods, serving as a contract between the shipper and the carrier.
- Document of title: It acts as legal proof of ownership, allowing the holder of the bill of lading to claim the goods upon arrival at the destination.
The importance of a Bill of Lading (BOL) is significant in the maritime laws of the shipping industry. It is often required before payment can be released, especially in international trade. And if any issues or disputes come up, this document is one of the first things referred to. It’s used as proof, and in many cases, it decides who legally owns the goods.
Who Regulates the Bill of Lading?
The bill of lading is regulated by both international rules and local laws. Some of the main international rules include the Hague Rules, Hague-Visby Rules, Hamburg Rules, and Rotterdam Rules. These set out the responsibilities and rights of the carrier.
Depending on the country and type of transport, local trade or shipping authorities may also have their own rules. Most shipping companies and freight forwarders also follow common industry standards to keep the process legally correct.
Example of Bill of Lading Document
Below is an example of what a typical Bill of Lading (BOL) document looks like:
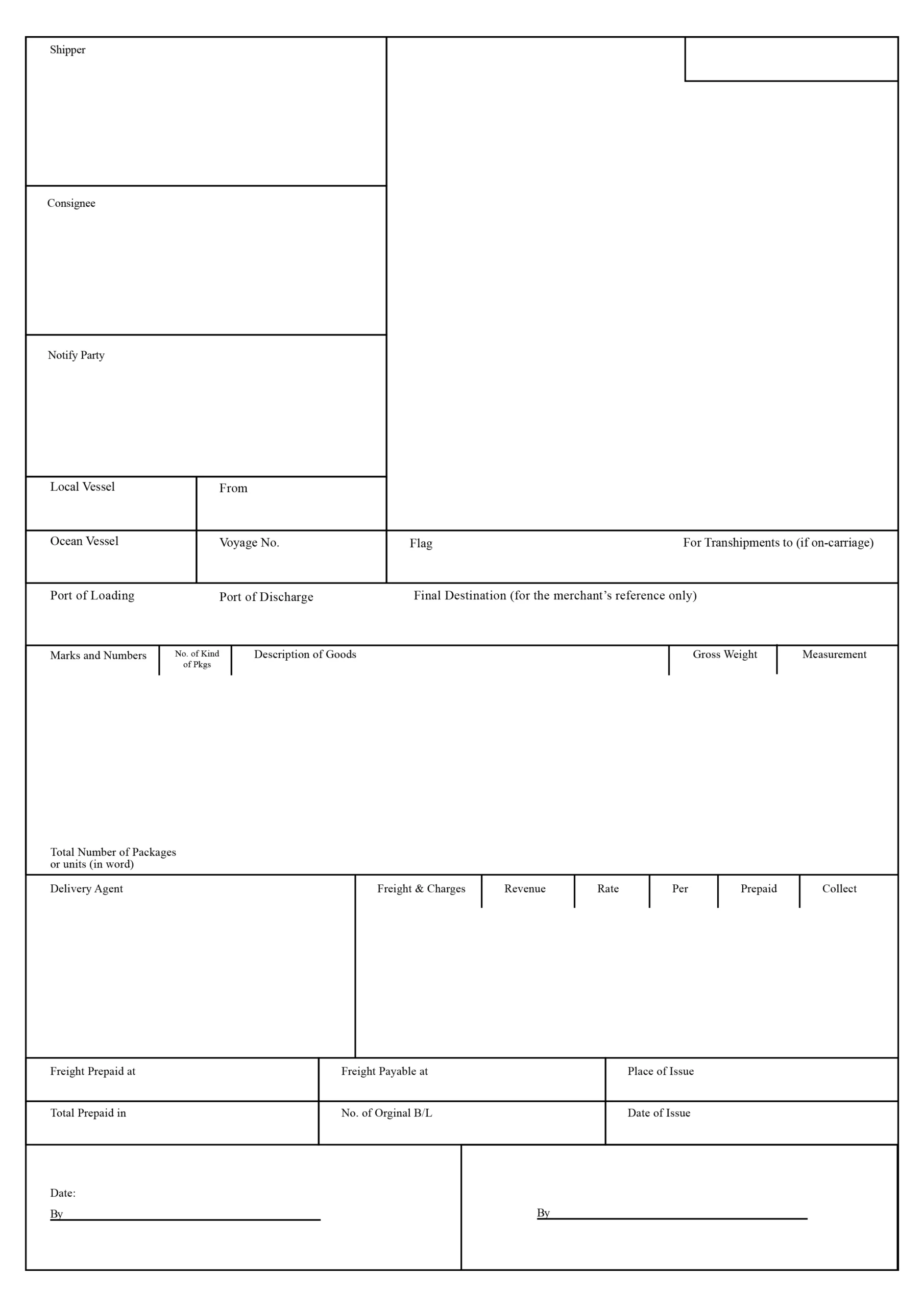
How do I fill out a Bill of Lading?
To fill out the bill of lading, start with the Ship From section by entering the name, address, and contact details of the sender. Include the SID# if applicable. Then, in the Ship To section, fill in the consignee’s name and full address, along with the CID# if known.
Under Third Party Freight Charges Bill To, include billing details if a different party is paying for the shipment. In the Carrier Name section, add the trailer number, seal number(s), SCAC, and Pro number (if provided by the carrier). Mark the appropriate freight charge terms (e.g., Prepaid, Collect, or 3rd Party).
In the Customer Order Information section, fill in the order numbers, number of packages, and whether each shipment has a pallet/slip (circle Y or N). In the Carrier Information area, provide the total number and type of packages, weight, and a description of the commodity being shipped.
Add the NMFC# and class for LTL (less-than-truckload) shipments. If applicable, enter the COD amount and choose whether the fee is to be collected or prepaid.
Finally, both the shipper and carrier should sign and date the form in the signature section, including trailer loaded and freight count details.
Note: The Bill of Lading is usually filled out by the shipper, carrier, or freight forwarding company, not by the customer. The example shown above is based on a standard BOL format, but the layout and details may vary depending on the shipping company. Still, the overall information you’re expected to provide remains more or less the same.
What Should Customers/Consignees Look for in a Bill of Lading?
As a customer or consignee, you need to review the Bill of Lading carefully before accepting the shipment. Check that your name and address are correctly listed, and make sure the description of the goods matches what you’re expecting, including quantity, packaging, and condition.
Also, confirm that the freight terms (like prepaid or collect) are accurate, so there are no surprise charges. If the BOL is negotiable (like an order bill of lading), make sure you or your representative has the right to claim the goods.
Once you review the BL document on your own, it will help you understand all the details and terms listed in the document. In the future, it will help you avoid disputes, delays, or issues with damaged or missing cargo.
Learn Logistics with Alliance Shipping
So, that was all about the Bill of Lading. We hope this blog helped you gain a better understanding of the BOL document and its importance. Alliance Shipping regularly covers various shipping topics to help you build a basic knowledge of key shipping terms.
If you’re interested in using our cargo shipping services from Dubai, UAE, feel free to contact us at +971 56 649 5103 or email us at manager.dxb@theallianceshipping.com.






















